.
Accessorizing and anchoring the LINC complex for multifunctionality.
Journal of Cell Biology,
2015 Jan 5;
208(1):11-22.
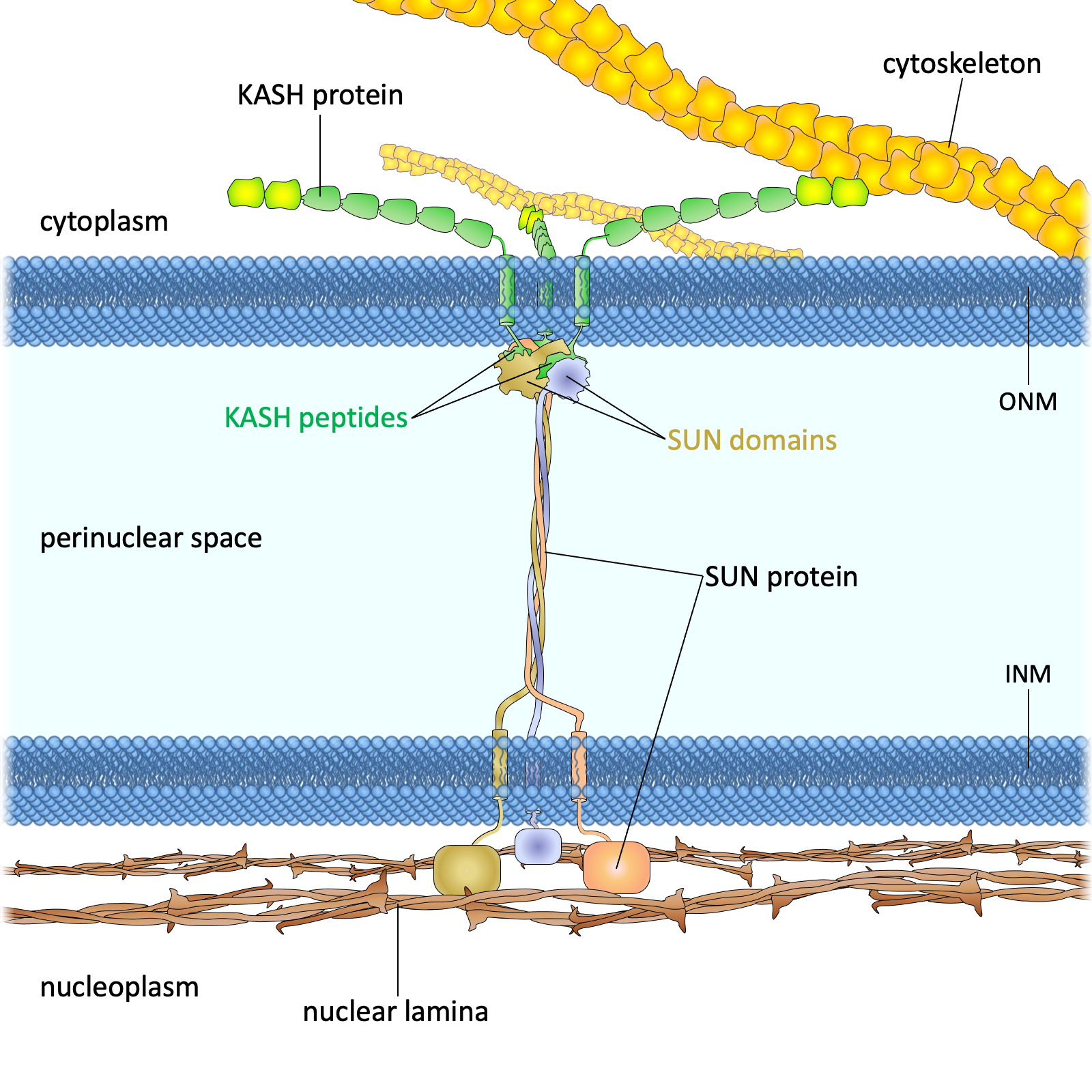
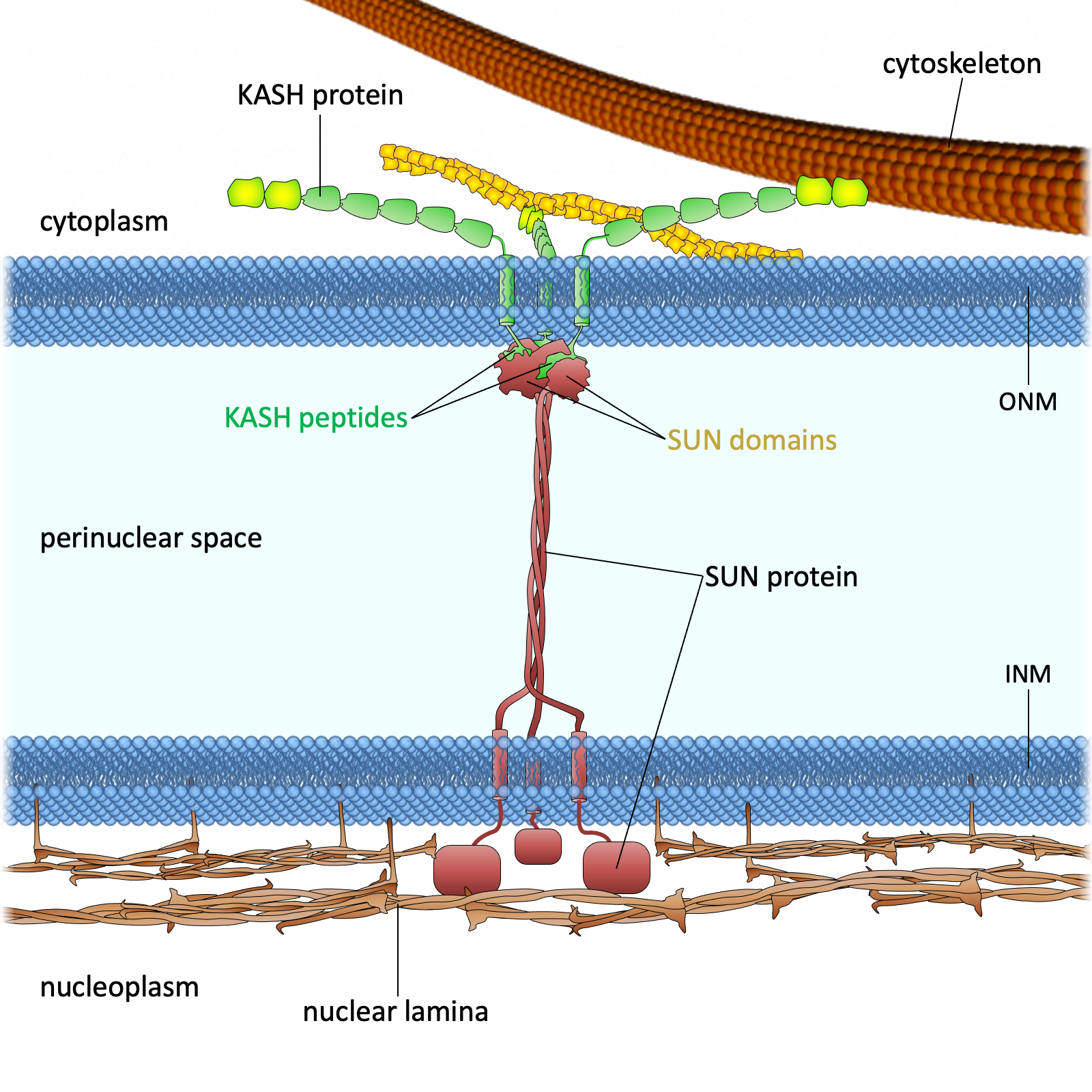
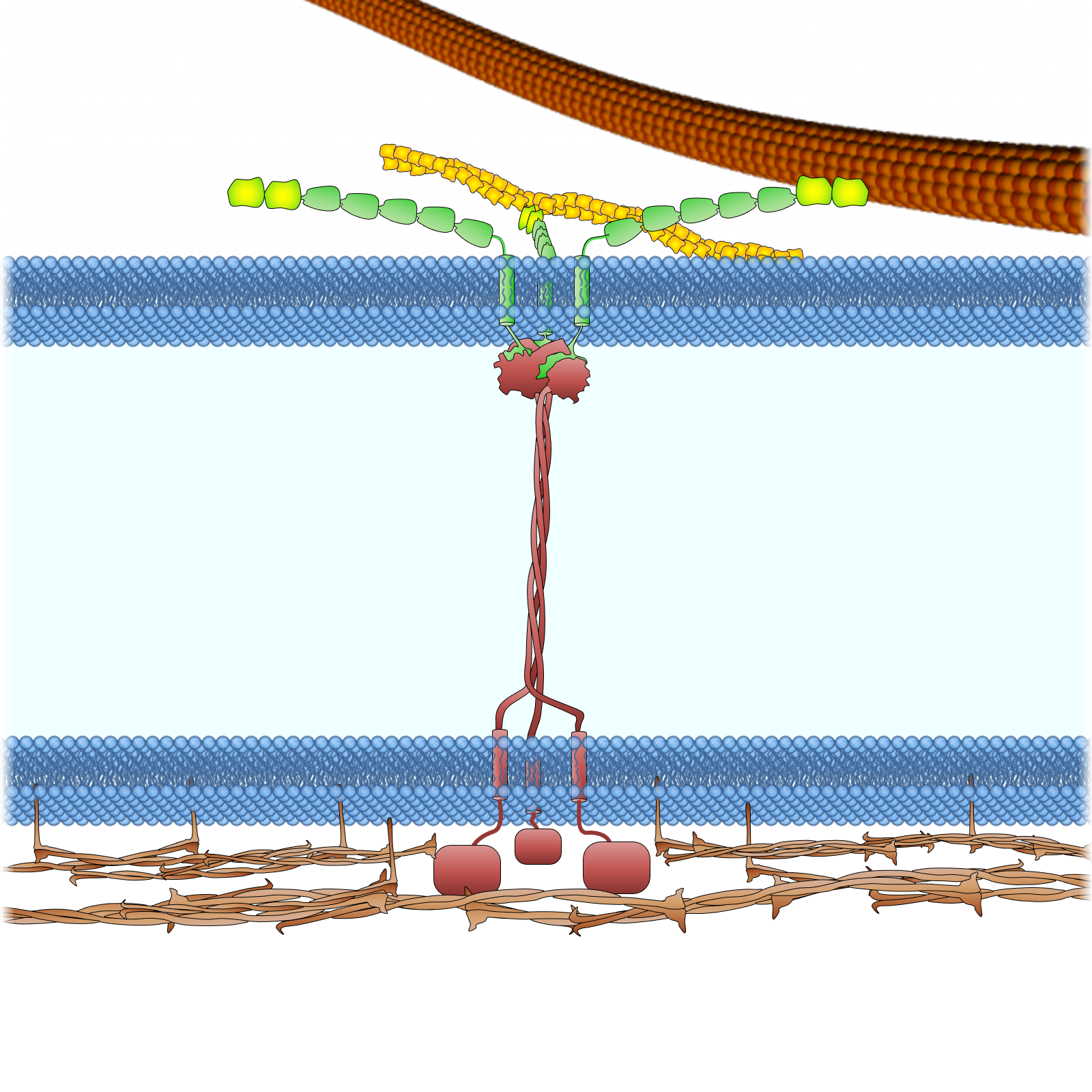
Figure 1. The LINC complex bridges the cytoskeleton and nucleoskeleton. The LINC complex is composed of KASH proteins in the outer nuclear membrane and SUN proteins in the inner nuclear membrane. The lumenal region of SUN proteins forms a triple helical coiled-coil, allowing trimerization of their SUN domains. The hydrophobic groove between neighboring SUN domains is required for the KASH peptide to bind, and this interaction is further strengthened by a KASH-lid of the SUN domain. The cytoplasmic extensions of KASH proteins vary in size and interact with different cytoskeletal elements. The nucleoplasmic domains of SUN proteins anchor the LINC complex to the nucleoskeleton, through its interaction with nuclear lamina, as well as chromosome-binding proteins and probably other anchoring proteins. INM, inner nuclear membrane; ONM, outer nuclear membrane.